

Blackapple Solutions is an IT Consulting company specialised in providing Testing Services to various clients across the globe. We are in the business from 2004. We work as testing partners to our clients and make sure their applications and systems work perfect.
Our expert Engineers and management team make sure to deliver the optimum solutions. We are based in the USA, Canada, UK, Netherlands, Romania, Brazil and India.

We offer Test Automation services to various clients.
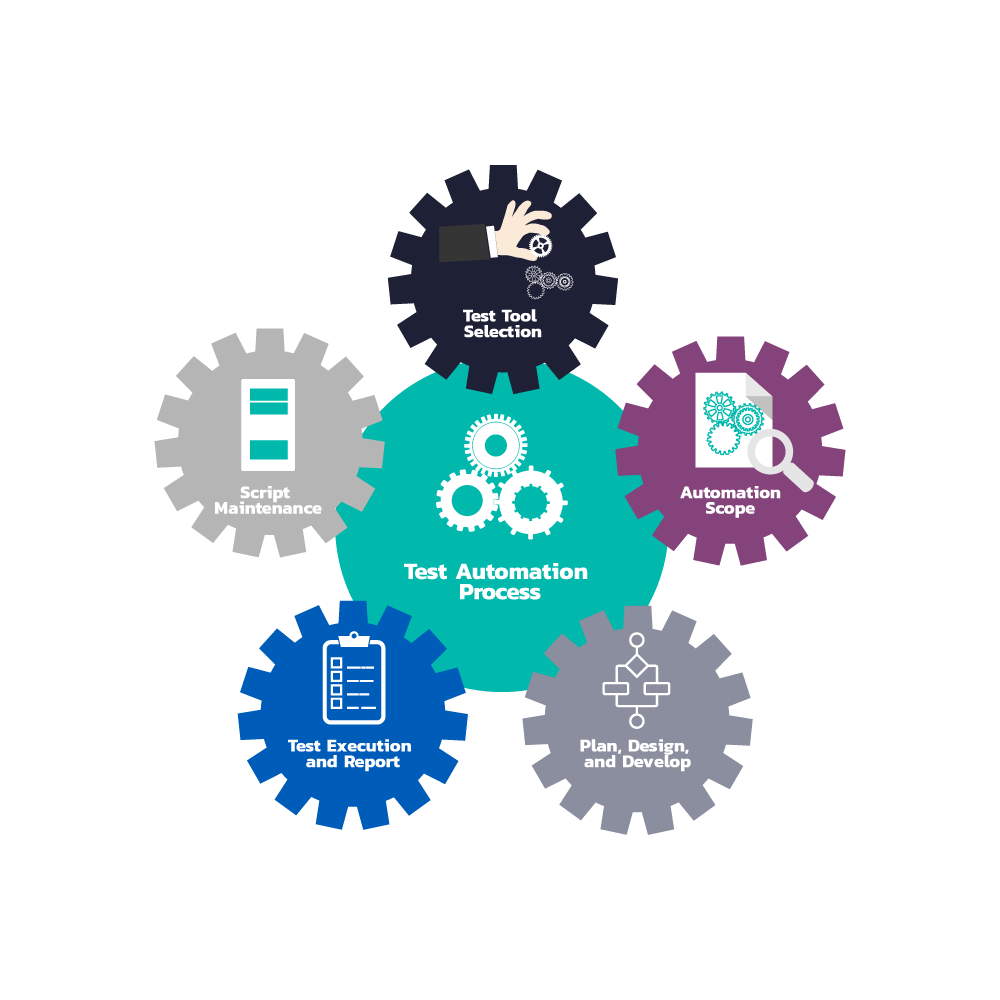
Software tests have to be repeated often during development cycles to ensure quality. Every time source code is modified software tests should be repeated. For each release of the software, it may be tested on all supported operating systems and hardware configurations. Manually repeating these tests is costly and time consuming. Once created, automated tests can be run over and over again at no additional cost and they are much faster than manual tests. Automated software testing can reduce the time to run repetitive tests from days to hours. A time savings that translates directly into cost savings.
We offer Automation Testing services by using various tools like Selenium, Appium, Cucumber, Siltest, Egg plant..etc.
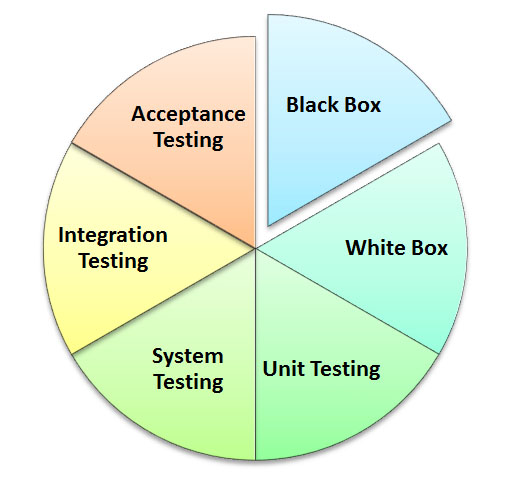
Manual Testing is a type of software testing in which test cases are executed manually by a tester without using any automated tools. The purpose of Manual Testing is to identify the bugs, issues, and defects in the software application. Any new application must be manually tested before its testing can be automated. Manual Software Testing requires more effort but is necessary to check automation feasibility.
Types of Manual Testing

We offer Performance Testing Services. Performance testing is a testing measure that evaluates the speed, responsiveness and stability of a computer, network, software program or device under a workload.
Without some form of performance testing in place, system performance will likely be affected with slow response times, experiences that are inconsistent between users and the operating system, creating an overall poor user experience. Determining if the developed system meets speed, responsiveness and stability requirements while under workloads will help ensure a more positive user experience.
Why use our performance testing services?
An organization can use performance testing as a diagnostic aid to locate computing or communications bottlenecks within a system. Bottlenecks are a single point or component within a system's overall function that holds back overall performance. For example, even the fastest computer will function poorly on the web if the bandwidth is less than 1 megabit per second. Slow data transfer rates might be inherent in hardware but could also result from software-related problems -- such as too many applications running at the same time or a corrupted file in a web browser.
FUNCTIONAL TESTING is a type of software testing that validates the software system against the functional requirements/specifications. The purpose of Functional tests is to test each business function of the software application, by providing appropriate input test data and verifying the output against the Functional requirements. This testing; checks User Interface, APIs, Database, Security, Client/Server communication and other functionality of the Application Under Test. The testing can be done either manually or using automation.


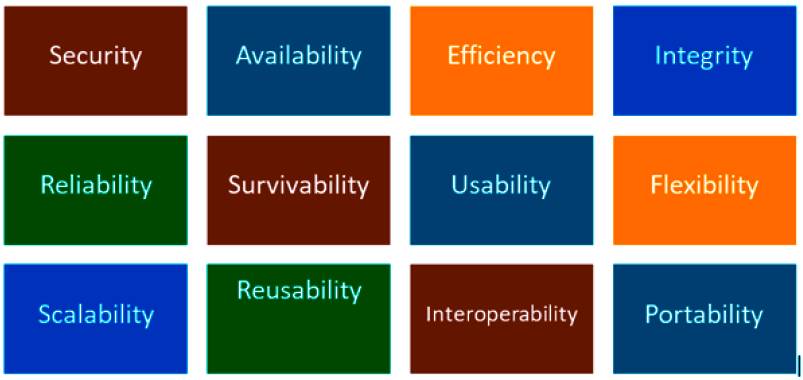
NON-FUNCTIONAL TESTING is defined as a type of Software testing to check non-functional aspects (performance, usability, reliability, etc) of a software application. It is designed to test the readiness of a system as per non-functional parameters which are never addressed by functional testing.
Mobile application testing is a process by which application software developed for handheld mobile devices is tested for its functionality, usability and consistency. Mobile app testing can be an automated or manual type of testing.


Telecom Testing is defined as the testing of Telecommunication software. Since the shift of the telecom sector to digital and computer networks, telecommunication industry uses software indispensable. Telecom sector depends on the various types of software components to deliver many services like routing and switching, VoIP broadband access, etc. Hence, telecom software testing is inevitable.
| Telecom Department | Telecom Activities |
|---|---|
| Pre-sales | It handles all the sales information like discounts, services, promos, etc. |
| Ordering | Applying for a new connection or disconnection a connection |
| Provisioning | This division deals with the physical connection between customers and TSP (Telecom Service Provider) |
| Billing | Under this division, all billing work is done |
| Service Assurance | In case of any failure, this division corrects the problem |
| Inventory Systems | It is the repository of all information |
| Tracking | This division tracks the ordering system and the status of an order. |